Learning Python was hard for me, but it didn’t have to be.
A decade ago, I was a fresh college grad armed with a history degree and not much else. Fast forward to today, and I’m a successful machine learning engineer, data science and deep learning consultant, and founder of Dataquest.
Currently, I am working on some deep learning projects, Marker and Surya. But let me be real with you—it wasn’t all smooth sailing. My journey to learn Python was long, filled with setbacks, and often frustrating.
If I could turn back time, I’d do things much differently. This article will guide you through the steps to learning Python the right way. If I had this information when I started, it would have fast-tracked my career, saved thousands of hours of wasted time, and prevented much stress.
Read this article, bookmark it, and then read it again. It’s the only Python learning guide you’ll ever need.
Why Most New Learners Fail
Learning Python doesn’t have to be difficult. If you’re using the right resources, it can be easy (and fun).
The Problem With Most Learning Resources
Many of the courses out there make learning more difficult than it has to be. Let me give you a personal example to illustrate my point.
When I first started learning to program, I wanted to do the things that excited me, like making websites or utilizing AI. Unfortunately, my course forced me to spend months on boring syntax. It was agony!
Throughout the course, Python code continued to look foreign and confusing. It was like an alien language. It’s no surprise I quickly lost interest.
Regrettably, most Python tutorials are very similar to this. They assume you need to learn all of Python syntax before you can start doing anything interesting. This is why most new learners give up.
An Easier Way
After many failed attempts, I found a process that worked better for me. I believe it’s the best way to learn Python programming.
The process is simple. First, spend as little time as possible memorizing Python syntax. Then, take what you learn and dive headfirst into a project you actually find interesting.
This minimizes the time spent on mundane tasks and maximizes the fun parts of learning Python. Think analyzing data, building a website, or creating an autonomous drone with artificial intelligence!
This better way of learning is why I built Dataquest. Our courses will have you building projects immediately with minimal time spent doing the boring stuff.
But how do you execute this learning process? The following five steps will explain everything you need to know. Your journey to learn Python starts now.
Step 1: Identify What Motivates You
With the right motivation, anyone can become highly proficient in Python programming.
As a beginner, I struggled to keep myself awake when trying to memorize syntax. However, when I needed to apply Python fundamentals to build an interesting project, I happily stayed up all night to finish it.
What’s the lesson here? You need to find what motivates you and get excited about it! To get started, find one or two areas that interest you:
- Data Science / Machine learning
- Mobile Apps
- Websites
- Computer Science
- Games
- Data Processing and Analysis
- Hardware / Sensors / Robots
- Automating Work Tasks


Step 2: Learn the Basic Syntax, Quickly
I know, I know. I said we’d spend as little time as possible on syntax. Unfortunately, we can’t avoid it entirely.
Here are some good resources to help you learn the Python basics without killing your motivation:
I can’t emphasize this enough: Learn what syntax you can and move on. Ideally, you will spend a couple of weeks on this phase but no more than a month.
The sooner you can start working on projects, the faster you will learn. You can always refer back to the syntax later if necessary.
Step 3: Make Structured Projects
Once you’ve learned the basic Python syntax, start doing projects. Applying your knowledge right away will help you remember everything you’ve learned.
It’s better to begin with structured projects until you feel comfortable enough to create your own.
Here are some examples of actual Dataquest projects. Which one ignites your curiosity?
Inspiration for Structured Projects
Remember, there is no right place to start when it comes to structured projects. Let your motivations and goals guide you.
Are you interested in general data science or machine learning? Do you want to build something specific, like an app or website? Here are some recommended resources for inspiration, organized by category:
Data Science / Machine Learning
- Dataquest — Teaches you Python and data science interactively. You analyze a series of interesting datasets, ranging from CIA documents to NBA player stats. You eventually build complex algorithms, including neural networks and decision trees.
- Scikit-learn Documentation — Scikit-learn is the main Python machine learning library. It has some great documentation and tutorials.
- CS109 — This is a Harvard class that teaches Python for data science. They have some of their projects and other materials online.
Mobile Apps
- Kivy Guide — Kivy is a tool that lets you make mobile apps with Python. They have a guide for getting started.
Websites
- Bottle Tutorial — Bottle is another web framework for Python. Here’s a guide for getting started with it.
- How To Tango With Django — A guide to using Django, a complex Python web framework.
Games
Invent Your Own Computer Games with Python — A book that walks you through how to make several games using Python.

Hardware/Sensors/Robots
Scripts to Automate Your Work
Projects are crucial. They stretch your capabilities, help you learn new Python concepts, and allow you to showcase your abilities to potential employers. Once you’ve done a few structured projects, you can move on to working on your own projects.
Step 4: Work on Python Projects on Your Own
After you’ve worked through a few structured projects, it’s time to kick things up a notch. Now, it’s time to speed up learning by working on independent Python projects.
Here’s the key: Start with a small project. It’s better to finish a small project than embark on a huge one that is never finished.
Tips to Discover Captivating Python Projects
I know it can feel daunting to find a good Python project to work on. Here are some tips to finding interesting projects:
- Extend the projects you were working on before and add more functionality.
- Check out our list of Python projects for beginners.
- Go to Python meetups in your area and find people working on interesting projects.
- Find open-source packages to contribute to.
- See if any local nonprofits are looking for volunteer developers.
- Find projects other people have made and see if you can extend or adapt them. Github is a good place to start.
- Browse through other people’s blog posts to find interesting project ideas.
- Think of tools that would make your everyday life easier. Then, build them.
Data Science/Machine Learning
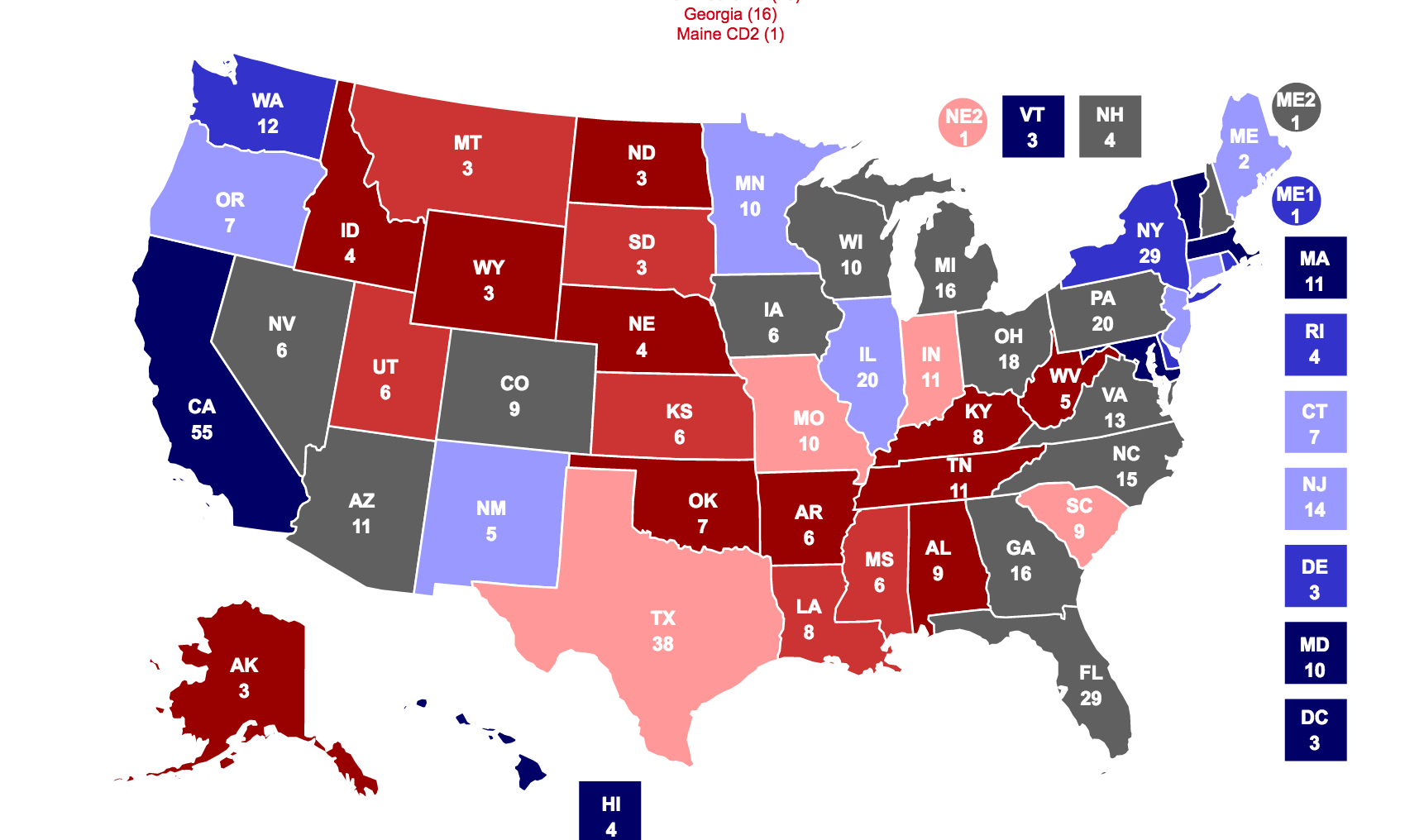
- A map that visualizes election polling by state
- An algorithm that predicts the local weather
- A tool that predicts the stock market
- An algorithm that automatically summarizes news articles

Mobile Apps
- An app to track how far you walk every day
- An app that sends you weather notifications
- A real-time, location-based chat
Website Projects
- A site that helps you plan your weekly meals
- A site that allows users to review video games
- A note-taking platform
Python Game Projects
- A location-based mobile game, in which you capture territory
- A game in which you solve puzzles through programming
Hardware/Sensors/Robots Projects
- Sensors that monitor your house remotely
- A smarter alarm clock
- A self-driving robot that detects obstacles
Work Automation Projects
- A script to automate data entry
- A tool to scrape data from the web
The key is to pick something and do it. If you get too hung up on finding the perfect project, you risk never starting one.
My first independent project consisted of adapting my automated essay-scoring algorithm from R to Python. It didn’t look pretty, but it gave me a sense of accomplishment and started me on the road to building my skills.
Obstacles are inevitable. As you build your project, you will encounter problems and errors with your code. Here are some resources to help you.
Resources If You Get Stuck
Don’t let setbacks discourage you. Instead, check out these resources that can help:
- StackOverflow — A community question and answer site where people discuss programming issues. You can find Python-specific questions here.
- Google — The most commonly used tool of any experienced programmer. Very useful when trying to resolve errors. Here’s an example.
- Python Documentation — A good place to find reference material on Python.
Step 5: Keep Working on Harder Projects
As you find success with independent projects, keep increasing the difficulty and scope of your projects. Learning Python is a process, and you’ll need momentum to get through it.
Once you’re completely comfortable with what you’re building, it’s time to try something harder. Continue to find new projects that challenge your skills and push you to grow.
5 Prompts for Mastering Python
Here are some ideas for when that time comes:
- Try teaching a novice how to build one of your projects.
- Ask yourself: Can you scale your tool? Can it work with more data, or can it handle more traffic?
- Try making your program run faster.
- Imagine how you might make your tool useful for more people.
- Imagine how to commercialize what you’ve made.
Final Words
Remember, Python is continually evolving. There are only a few people in the world who can claim to understand Python completely. And these are the people who created it!
Where does that leave you? In a constant state of learning and working on new projects to hone your skills.
Six months from now, you’ll look back on your code and realize how terrible it is. At this point, you’ll know you’re on the right track.
If you thrive with minimal structure, then you have all you need to start your journey. However, if you need a little more guidance, our courses may help.
I founded Dataquest to help people learn quickly and avoid the things that make people quit. Our courses will have you writing actual code within minutes and completing real projects within hours.
If you want to learn Python to become a business analyst, data analyst, data engineer, or data scientist, we have career paths designed to take you from complete beginner to job-ready in months.
Common Questions about Learning Python (FAQs)
Why should I learn Python?
1. You Can Automate Tasks
Python is a versatile programming language, which means there’s something in it for everyone. Once you learn Python, you’ll be able to do the following:
- Work with massive datasets easily.
- Scrape data from the web and access APIs
- Use it to power-up your work in Excel
- Automate all sorts of tasks.
Learning to automate tasks independently can be incredibly powerful because your time is valuable. Let the robots send your emails and fetch data from the internet. And if you’re feeling extra ambitious, you can even create the next coffee delivery app to get your caffeine fix every morning easily. (That may take a little bit more work, though.) More likely, you’ll be able to start finding creative solutions for the people and companies you work for. When you learn Python, you’re literally learning a new language that is built on identifying and predicting patterns. As you find patterns, you’ll be able to communicate those findings in a way that makes a big impact in your industry and the world.
2. You Can Impress Your Boss
Learning Python is also a great way to impress at work (or get that promotion you’ve been vying for). To those who can’t code, the ability to program sometimes seems like a superpower. Programming gives you the ability to leverage your knowledge and multiply your output. With it, you may be able to get ten times as much work done in the same amount of time. As we mentioned above, when you learn Python, you’ll be able to gather data quickly and translate the numbers to real-world solutions. For example, in a business setting, you could add value by doing things like web scraping, sending emails automatically, or even analyzing supply chain production to find missed opportunities for cost savings or quality control. If your boss has mentioned that understanding data science could help you move toward your career goals, a self-paced Python course that helps you learn Python online could be the perfect way to balance a data career and personal development.
3. It Creates Exciting New Career Opportunities
If you’re looking for an entirely new career or maybe aren’t feeling fulfilled in your current job, you’ve come to the right place. Demand for Python developers, especially in the data science field, has never been higher. Data science is rewarding, and it pays exceptionally well. These opportunities are sometimes available remotely, so you can work from anywhere for a U.S. company without being tied to a U.S. location. Data science is a relatively new field, and with that freshness comes modern hiring practices. An emphasis on understanding your craft and being able to drive results is slowly beginning to trump the need for a four-year degree and an office down the hallway. We’ve seen many of our alumni find rewarding careers (either in an office or remotely) after completing our Data Science paths. In fact, we’ve structured our courses to help you leave with a leg up on the job hunt. You’ll have experience working with real-world data and a portfolio full of finished data science projects. For human resources offices evaluating your resume, this can be far more important than your degree.
4. Build the foundation to learn AI and Machine learning

In the age of generative AI, Python’s significance in 2024 cannot be overstated. It serves as the foundation for AI and machine learning, with key frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch relying on Python for development and innovation. Its effectiveness in automating tasks and analyzing large datasets is crucial for training AI models. Python’s seamless integration with AI tools and its widespread use in AI research makes it indispensable for anyone involved in this field. The language’s extensive community support, resource availability, and versatility across various domains, including web development and data science, further enhance its importance. Additionally, understanding Python is vital for navigating the ethical and governance aspects of AI, ensuring responsible development and application of AI technologies. Thus, Python’s role extends beyond mere programming, becoming a crucial tool for shaping and understanding the future of AI.
Is it hard to learn Python?
Learning Python can certainly be challenging. However, if you take the step-by-step approach I’ve outlined here, you’ll find that it’s much easier than you think. Python is actually considered one of the easiest programming languages to learn. While anyone can learn Python programming — even if you’ve never written a line of Python code before — you should expect that it will take time, and you should expect moments of frustration.
Can you learn Python for free?
There are many free Python learning resources. At Dataquest, for example, we have dozens of free Python tutorials.
The downside to free resources is the lack of structure; you’ll need to patch together several free resources. This means you’ll spend extra time researching what you need to learn next and how to learn it. It may find that you’ve wasted time learning the wrong things or often get stuck because you lack the prerequisite knowledge to complete a project or tutorial.
Premium platforms may offer better teaching methods (like the interactive, in-browser coding Dataquest offers) and save you time finding and building your own curriculum.
Can you learn Python from scratch (with no coding experience)?
Yes. Python is a great language for programming beginners because you don’t need prior experience with code to pick it up. Dataquest helps students with no coding experience get jobs as data analysts, data scientists, and data engineers.
How long does it take to learn Python?
If you’re looking for a general answer, here it is: Learning the Python basics may only take a few weeks. However, if you’re pursuing a career as a programmer or data scientist, you can expect it to take four to twelve months to learn enough advanced Python to be job-ready. (This estimate comes from learners who have taken our Python for Data Science path.)
The personalized answer depends on several factors. The good news: it is probably less than you think if you take the right approach. Let’s look at some examples …
- A Marketer Who Wants an Edge: If you’re a marketer who’d like to analyze Google Analytics data more rigorously, you could learn fundamental Python syntax and the required pandas techniques in a matter of weeks. This wouldn’t make you a job-qualified Python developer or data analyst, but it would be enough to solve your problem.
- A Begineer Seeking a New Career in Data Science: If you’re learning from the beginning and are looking for full-time work using Python, you can expect to spend at least a few months studying part-time. How many months will depend on the job you’re looking for. Working through our Data Analyst in Python course path, for example, would prepare you to apply for jobs as a Data Analyst. Most learners take at least three months to complete this path. To be clear, though, you could spend a lifetime learning Python. There are hundreds of libraries, many of them regularly improving and evolving, and the language itself also changes over time. It doesn’t take too long to become capable of solving problems with Python, but to master Python means continually learning and growing over the course of your career.
- Exploring a career in web development or software engineering: If you’re keen on web development and want to learn Python’s role in it, our AI Development with Python path is a great place to start. In weeks, you’ll grasp Python fundamentals tailored for web development, work with numerical and text data, make API calls to the web, and build your own projects.
Is learning Python still worth it?
Yes. Learning Python is worth it from a career outlook, financial return, and versatility perspective.
- Demand for Python skills is High: In 2024, Python’s importance in the tech industry is indisputable, particularly in fields like machine learning and artificial intelligence, where it’s the language of choice for many. Its usage has seen a significant 22.5% year-over-year increase, reflecting its widespread adoption across various industries. Professionals proficient in Python are highly sought after, with the machine learning job market alone projected to reach $31 billion by 2024. Python skills not only open doors to diverse and lucrative career opportunities but also enhance overall employability. With Python’s applications spanning multiple roles—from data analysis to software development—learning this versatile language is an invaluable investment for any tech-focused career in today’s evolving job market.
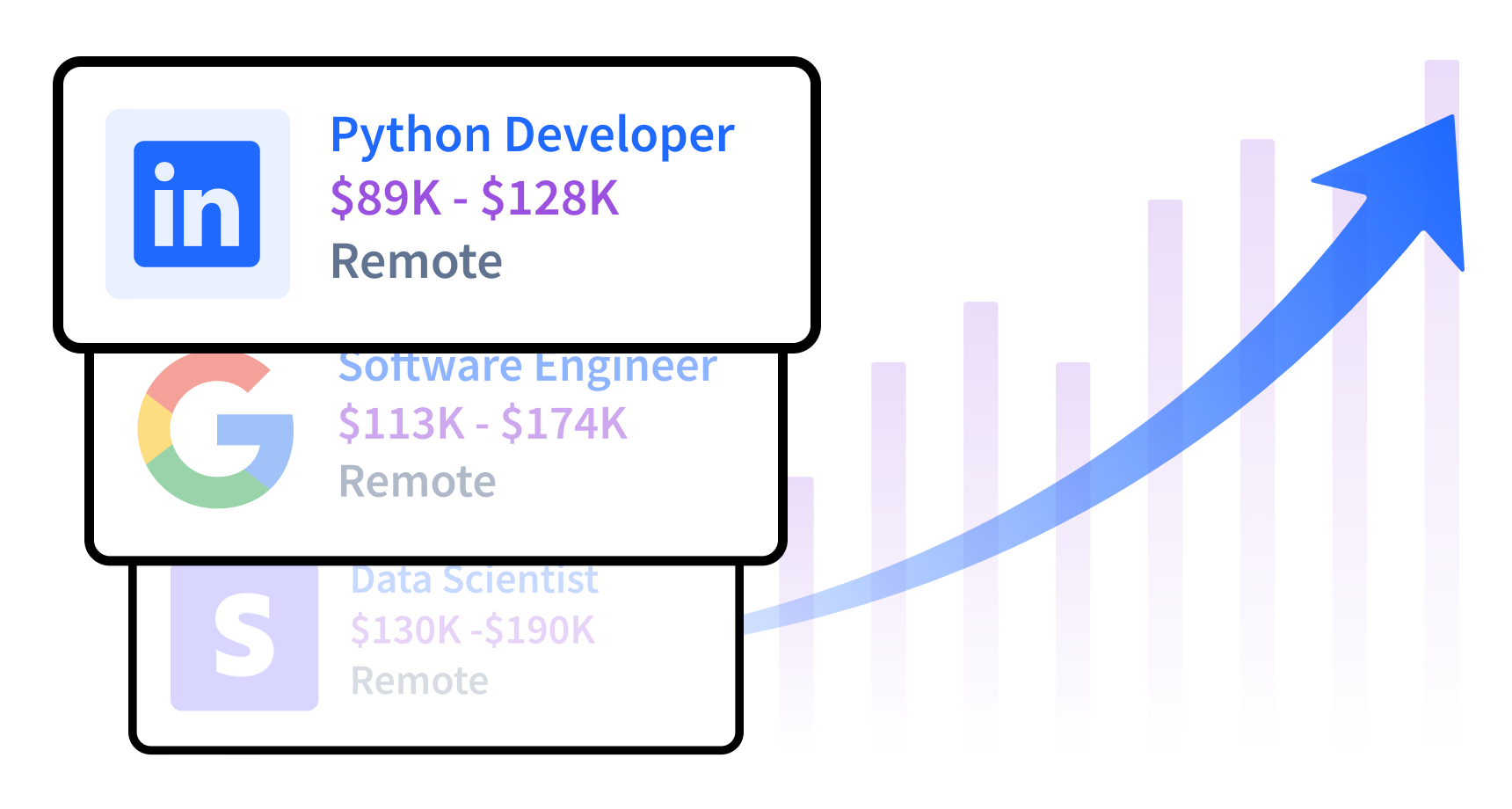
- Lucrative Salaries: Careers that require Python skills can earn salaries well over $100,000 per year in the United States. Here’s a list of jobs requiring Python programming knowledge — and their U.S. salaries:
- Software Engineer: $113K–$174K
- Entry Level Data Analyst: $55K–$83K (become one here)
- Data Analyst: $66K–$103K (become one here)
- Data Engineer: $103K–$152K (become one here)
- Data Scientist: $130K–$190K (become one here)
- Python Developer: $89K–$128K
- Deep Learning Engineer: $118K–$181K
- Machine Learning Engineer: $124K–$186K
- Incredible Versatility: There’s an inside joke in the Python community that Python is the second-best language for everything. Of course, what’s best is subjective, but Python is incredibly flexible. It’s the most commonly used language for data science and machine learning. One reason for its widespread popularity is that it’s one of the easier languages to learn and use when working with data. And, fortunately for employers and data scientists alike, it doesn’t require years of study to master.

Can you teach yourself Python?
Yes, it’s very possible to learn Python on your own. There are many learning resources available on the web to help you learn Python for everything from web development to artificial intelligence. Here at Dataquest, we’ve helped thousands of students learn Python and get jobs in data science, all on their own schedules and from the comfort of their own homes. Teaching yourself Python does take time, though. You must also be sure that you’re writing code and applying what you learn in real-world scenarios rather than just watching lecture videos and answering multiple-choice questions. Taking the right approach to learning Python can also be the difference between success or failure when you’re learning through self-study.
Do you have any tips on learning Python faster?
If you’re learning Python on your own, creative time-management habits will be very helpful — especially if you want to learn Python sooner rather than later. While five hours may seem like a lot to fit into your already-busy weekly schedule, it’s very achievable for someone working a full-time job — or with a full calendar of school commitments. Here are a few ways you might find the spare hours …
- Set your alarm alock for 30 minutes earlier: The best time you can set aside to learn Python each day is in the morning. Biologically, your best, most productive time is around the first two hours of each day. You don’t want to sacrifice any sleep, but you may want to get to bed earlier so you can practice a bit before work. It’s a commitment, for sure. But, if you set aside your clothes the night before, have your coffee ready to go, and already know what aspects of Python you are going to work on, it’s a bit easier. Tell yourself that you can’t look at your phone or emails until you dedicate 30 minutes to learning Python, and make it a habit! The time it saves and the advancement in your career will be worth the extra effort. As an added benefit, you’ll feel extra healthy when you get a productive head start on your day.
- Log off your evening Netflix habit: If you already wake up at 5 am to get to work each day, waking up earlier may not be the best option for you. In that case, you might take the first two hours when you get home from work each day to learn Python. If you’re overwhelmed by the idea of finding two hours between your commute, gym, dinnertime, and downtime, spend a week really looking at how you spend your evenings. Write down exactly what you did each day this week:
- How much time did you spend on Netflix?
- Did you waste a few hours on social media?
- Did you get lost scrolling through Amazon?
- Can you prepare your meals on Sunday to cut back on weeknight cooking?
- Take advantage of quiet Saturday mornings: We’ve seen that practicing every day is the best way to master Python as quickly as possible. It’s important to be consistent, but sometimes life gets in the way. That’s what weekends are for. If you’re completely booked from 5 am to 6 pm every day, you can keep yourself on track by putting in extra hours on the weekend. Plus, this is a great way to find uninterrupted time in a space you’ve dedicated just for learning Python. One thing to keep in mind: studying two hours a day is far better than ten hours in one day on the weekend. If you have other commitments during the week, even ten minutes each morning will make a difference compared to only looking at Python materials once a week.
- Join A Community of Python Programmers: Joining a community of Python developers will help you stay on track toward your goal to learn Python. Python meetups are fairly common on Meetup.com, and you’ll get recommendations from other members of these groups. Additionally, Dataquest’s students use our Members’ community to network and discuss Python problems, troubleshooting, and data science portfolio projects. If you carve out a few minutes each day for networking, you’ll complete your coursework with a new skill and a new network as you enter the job market!
- Find a Project you are interested in working on: The best way to learn how to complete data projects is by building data projects. Dataquest learners spend their time working through real-world data challenges that teach learners to combine multiple skills and tools to solve a problem or accomplish a task. Projects created out of genuine curiosity stand out, as opposed to those made just for the sake of it. Take your time to find a topic that captures your attention or choose from hundreds of data science projects on the Dataquest learning platform.
- Compete on Kaggle: Kaggle hosts data science competitions. Signing up is free, and members submit Python scripts to find the best model for a given dataset. You’ll find a lot of competitions with objectives similar to the guided projects in your Dataquest portfolio. If you’re one of those Fortnite fans we mentioned above, collaborating with other Dataquest students on Kaggle competitions can help replace some of your game time in a way that helps you learn Python without losing that competitive fix!
Do you need a Python certification to find work?
Probably not. In data science, certificates don’t carry much weight. Employers care about skills, not paper credentials.
Translation? A GitHub full of great Python code is much more important than a certificate.
What types of jobs can you get knowing Python?
Many jobs can benefit from Python skills. Here are a few careers that you can break into if you know Python:
- Python Developer
- Data Analyst
- Data Scientist
- Data Engineer
- Business Analyst
- Machine Learning Engineer
- Software Engineer
Is Python relevant outside of data science/machine learning?
Yes. Python is a popular and flexible language that’s used professionally in a wide variety of contexts.
We teach Python for data science and machine learning, but you can also apply your skills in other areas. Python is used in finance, web development, software engineering, game development, and more.
Having some data analysis skills with Python can also be useful for various other jobs. If you work with spreadsheets, for instance, there are likely things you could be doing faster and better with Python.
Where can you learn basic Python programming?
Plenty of online Python courses, books, boot camps, and free guides online exist. We always recommend Dataquest, but we’re a bit biased.
Basic Python skills you’ll need to learn include:
- Python lists
- Python loops
- Python strings
- Python functions
- Python arrays
- Python operators
- Python syntax
- Etc
Here at Dataquest, we teach the basics while expediting the time required to apply what you learned with a fun project. Try our introductory Python course here.

